LIGHT AND HUMAN EYE
LIGHT AND HUMAN EYE
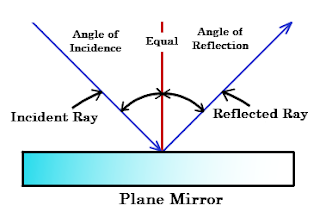
1 Law of reflection
1. Angle of incidence is equal of angle of reflection
2. Incident ray , reflected ray and normal ray lie
on same point
Multiple images are formed when we put the
object between two mirrors. The number of Image formed is depends on angle
between the mirror.
Number
of Image = 360/Angle -1
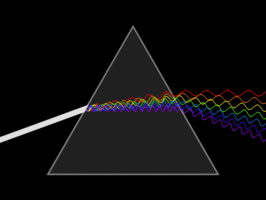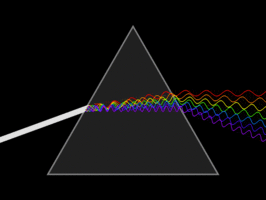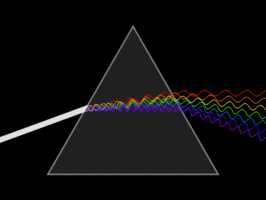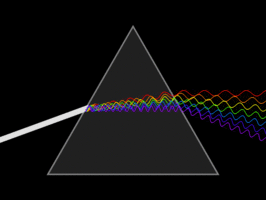
White light is a mixture of
seven colour. When we pass the light through light disperse in seven original
colour. Violet,Blue, Indigo, Green,Yellow,Orange,Red.
Cornea- The outer transparent part of eye under which Iris, lens
etc lie.
Pupil- It allow light to enter in retina.
Iris- It is part of eye which controls the amount of light enter
in eye by controlling the pupil. It shrink when asses light enter in eye and it
became expand when amount of light decrease. The colour of eye is nothing but
the colour or lris.
Retina- it seems like screen where Image is formed.
Lens- It helps in converging the light on retina like projector.
Ciliary muscle- It control the lens and help the lens to form the
Image on retina.
Optic nerve- It send the message of sight to the brain after
that brain work on that information.
There are two types of cells
Rod cell - These are sensitive to dim light.
Cones cell- These are sensitive to bright light
Blind spot- At the junction of the optic nerve and the retina, there
are no sensory cells, so no vision is possible at that spot. This is called the
blind spot.
Persistence of vision is 1/16. Our
eye can see 16 images in one second.
The most comfortable distance at which one can read with a
normal eye is about 25 cm.
Myopia- It is also called shortsightedness. In which person can see
nearby object clearly but can’t see far object clearly.
Hypermetropia – It is also called farsightedness. In which person can see
far object clearly but can’t see nearby clearly.
Sometimes, particularly in old age, eyesight becomes foggy.
It is due to the eye lens becoming cloudy. When it happens, persons are said to
have cataract.
Braille
System
This system is developed for visually challenged
people this methods depend upon recognition by touching. Each character has to
be memorised. Braille texts can be produced by hand or by machine. Type writer
- like devices and printing machines have now been developed.
Point 11 and 12 are given for visually challenged people.
They touch it and recognize the note.





Comments
Post a Comment