Cell key concept "biology"
Cell- it is a structural and functional unit of life is called cell.
Cells may be compared to bricks. Bricks are assembled to make a building.Similarly, cells are assembled to make the body of every organism.
Robert Hooke in 1665 observed slices of cork under a simple magnifying device.
The egg of a hen represents a single cell and is big enough to be seen by the unaided eye.
Scientist use microscopes which magnify objects. Stains (dyes) are used to colour parts of the cell to study the detailed structure.
Human body has trillions of cells which vary in shapes and sizes. Different groups of cells perform a variety of functions. That combination of cell is called tissue
Organisms made of more than one cell are called multicellular. ex-man, cat, dog etc.
The single-celled organisms are called unicellular. Ex- ameba, paramecium etc.
A single-celled organism, like amoeba, captures and digests food, respires, excretes, grows and reproduces. Similar functions in multicellular organisms are carried out by groups of specialised cells forming different tissues
. The largest cell measuring 170 mm ×130 mm, is the egg of an ostrich.
Size of cell is depend on function not on the shape of the organism. Ex - nerve cell of elephant and rat is equal in size perform same function transfer of massage.
Group of tissue make organ and group of organ make organ system Each organ in the system performs different functions such as digestion, assimilation and absorption. Similarly, different organs of a plant perform specific/specialised functions. For example, roots help in the absorption of water and minerals.
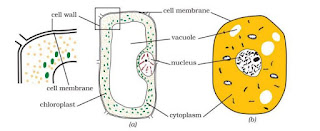
The basic components of a cell are cell membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus The cytoplasm and nucleus are enclosed within the cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane. The membrane separates cells from one another and also the cell from the surrounding medium. The plasma membrane is porous and allows the movement of substances or materials both inward and outward.
In addition to the cell membrane, there is an outer thick layer in cells of plants called cell wall for protection.
Nucleus is an important component of the living cell. It is generally spherical and located in the centre of the cell.
Nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane called the nuclear membrane. This membrane is also porous and allows the movement of materials between the cytoplasm and the inside of the nucleus.
A smaller spherical body in the nucleus. It is called the nucleolus. In addition, nucleus contains thread-like structures called chromosomes. These carry genes and help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
The cells having nuclear material without nuclear membrane are termed prokaryotic cells.
well organised nucleus with a nuclear membrane are designated as eukaryotic cells.
Large vacuoles are common in plant cells. Vacuoles in animal cells are much smaller it is due to vacuole used to store food.
Several small coloured bodies in the cytoplasm of the cells of Tradescantia leaf. They are scattered in the cytoplasm of the leaf cells. These are called plastids. Green plastids are called chloroplast

Comments
Post a Comment